Introduction
This document serves as a step-by-step guide for system administrators and accountants tasked with setting up Odoo's accounting module for an Australian-based business. It focuses on the critical settings that must be reviewed and configured after the initial Australian fiscal localization package has been applied. While the localization package provides an excellent foundation, a thorough review and adjustment of these settings is essential to tailor the system to your company's specific operational requirements and ensure full compliance with Australian business practices.
1.0 General Tax Settings Configuration
1.1 Strategic Importance of Tax Settings
Correctly configured tax settings are the bedrock of your financial system's integrity and compliance. These configurations form the foundation for Goods and Services Tax (GST) compliance, directly impact the profitability of your pricing strategies, and automate tax reporting for accurate Business Activity Statements (BAS). A failure here can lead to significant rework during tax season and potential compliance issues. While Odoo's localization provides robust defaults, fine-tuning these settings ensures transactional accuracy from day one and saves significant administrative time in day-to-day operations
1.2 Configuring Default Taxes and Pricing Display
The Default Taxes setting is a critical function that automates the application of tax rates to new products, preventing manual errors and ensuring consistency.
- By default, the Australian fiscal localization package sets both sales and purchase taxes to 10% GST. You have the option to change these defaults if your company's specific requirements differ (for example, if a majority of your products are GST-free).
- A key strategic choice is whether to display product prices as GST inclusive or exclusive. This decision impacts how prices are presented to customers and must be made early. It's crucial to understand that once the first transaction is recorded, the global setting in this menu can no longer be changed directly. However, an expert consultant knows a common workaround: while the global default is locked, tax display can still be managed through individual tax configurations.
1.3 Defining Tax Rounding Methodology
The Rounding Method setting determines how Odoo calculates tax on invoices with multiple lines. You can choose between two options:
-
Rounding Per Line:
This method rounds the calculated tax on each individual invoice line. This is the advised method if your product prices are set as tax-inclusive.
- On the Total Amount:
This method calculates the tax on the subtotal of the entire invoice.
This setting offers flexibility, as it can be adjusted at any time, even after transactions have been posted.
1.4 Implementing Cash Basis Accounting for GST
Odoo's default accounting method is accrual basis; however, for businesses that manage GST on a cash basis, the Cash Basis option can be enabled.
- This setting is typically enabled by businesses that report and pay GST based on the cash they have actually received or paid out, rather than on invoices issued or bills received.
-
Activating this option triggers two system changes: Odoo automatically creates a dedicated cash basis journal, and a new field, Base Tax Received Account, appears in the settings.
-
The Base Tax Received Account functions as a temporary holding account. It segregates the tax amounts from unpaid invoices and bills from those that have been paid, ensuring that GST reporting accurately reflects the cash position of the business, in line with cash basis accounting rules.
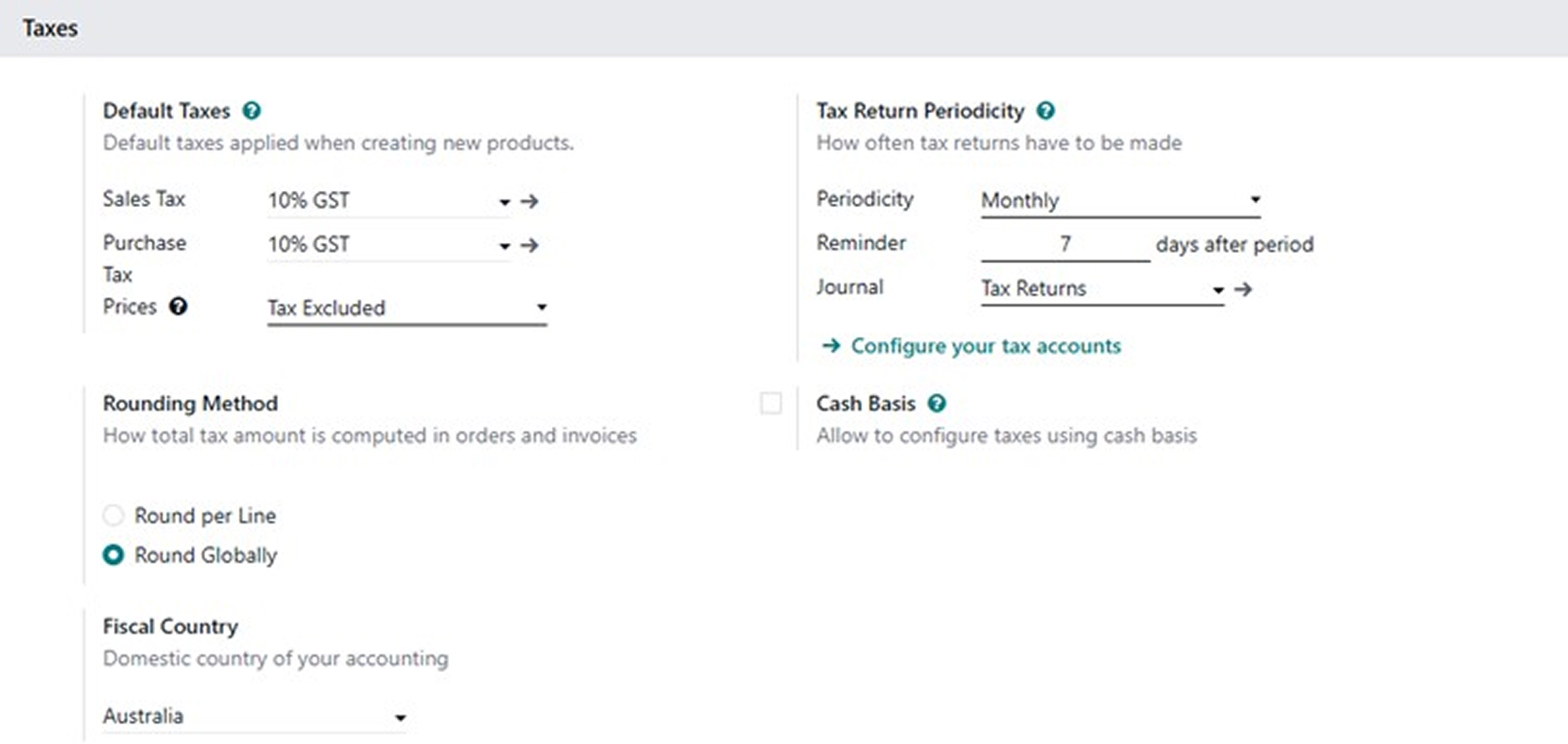
1.5 Setting the Tax Return Schedule
The Tax Return Periodicity settings dictate your company's GST filing schedule and associated system actions.
Setting | Function | Australian Default |
Periodicity | Determines the frequency of GST return filing (Monthly, Quarterly, or Annually). | Monthly |
Reminder | Sets a user reminder, in days, to lodge the return after a period closes. | 7 Days |
Journal | Specifies the journal used to post the period closing entry. | Miscellaneous Journal (Tax returns) |
1.6 Verifying Fiscal Country and Identifying Irrelevant Settings
First, ensure the Fiscal Country is correctly set to Australia, which should be automatically populated by the localization package. Beyond this, several tax settings are not applicable to Australian businesses and can be ignored.
Settings to Disregard for Australian Localization
- AVA Tax
- EU Intra-community Distance Selling
- Verify VAT Numbers
With tax and compliance settings established, we can now turn to the management of currencies for international trade.
2.0 Currency Management
2.1 Strategic Importance of Currency Settings
For any business engaged in international trade, proper currency configuration is non-negotiable. These settings are crucial for ensuring the accuracy of financial reporting, actively managing and mitigating foreign exchange risk, and streamlining transactions with overseas partners. A well-configured system automates rate updates, protecting your profit margins from currency volatility and eliminating error-prone manual calculations.
2.2 Main Currency and Automatic Rate Updates
- The Australian fiscal localization package automatically sets the Main currency to Australian Dollars (AUD).
- For companies dealing in multiple currencies, enabling the "Automatic Currency Rates" feature is highly recommended. This allows Odoo to automatically update exchange rates from a third-party provider, ensuring that foreign currency transactions are converted accurately.
After enabling this feature, you must configure the following:
- Service: Select an exchange rate provider. Odoo offers around 26 different providers, but for Australian businesses, xe.com is generally the most appropriate and widely used option. If you prefer to manage rates manually, you can leave this field blank.
- Interval: Choose the frequency for rate updates. The available options are Manually, Daily, Weekly, and Monthly. This setting dictates how often Odoo will pull new rates, which are then applied to all foreign transactions recorded during that period.
Having configured currency management, we will now focus on the settings that define how you interact with your customers through invoices and payments.

3.0 Customer Invoice and Payment Configuration
3.1 Strategic Importance of Customer-Facing Settings
The configurations in this section directly impact cash flow, operational efficiency, and the customer experience. They define the entire lifecycle of a customer transaction—from how an invoice is generated and delivered to how payment is received and processed. A thoughtful setup can accelerate payment times, reduce your Days Sales Outstanding (DSO), and present a professional, modern image to your clients.
3.2 Enhancing Customer Invoices and Communication
These settings control the appearance, content, and delivery methods for customer invoices.
- Snailmail: This In-App Purchase (IAP) service allows you to send physical invoices and follow-up reports via postal mail directly from Odoo. It requires prepaid credits to function. You can customize the physical mailings with the following options:
- Print in Colour
- Print on Both Sides
- Add a Cover Page
- Invoice Online Payment: Enabling this feature significantly streamlines the payment process by adding a "Pay Now" button to the customer portal. This requires integrating a payment provider (e.g., Stripe, PayPal).
- A sub-option, "Add QR Code link on PDF", can be enabled to include a scannable QR code on printed invoices, which directs customers to the online payment portal.
- A sub-option, "Add QR Code link on PDF", can be enabled to include a scannable QR code on printed invoices, which directs customers to the online payment portal.
- Default Terms and Conditions: You can add standard T&Cs to documents like invoices and quotations in two ways:
- Add a Note: Enter your terms and conditions as plain text directly into a text box.
- Add a Link to a Web Page: Insert a URL that links to an external webpage containing your T&Cs.
- Add a Note: Enter your terms and conditions as plain text directly into a text box.
- Aesthetic and Legal Formatting: The following settings enhance the professionalism and compliance of your documents:
- Total amount of invoices in letters: Displays the invoice total in words (e.g., "One Hundred and Ten Dollars").
- Authorized Signatory on invoice: Adds a legal signatory to the bottom of documents.
- Taxes in company currency: On invoices issued in a foreign currency, this displays the untaxed amount, tax, and total in both the foreign and the main company currency (AUD).
- Total amount of invoices in letters: Displays the invoice total in words (e.g., "One Hundred and Ten Dollars").
3.3 Managing Customer Accounts and Payments
These settings govern customer credit, payment processing, and specific invoicing scenarios.
- Sales Credit Limit:
- This enables a global credit limit check for all customers, triggering an alert if a new sales order or invoice would cause a customer to exceed their limit.
- Crucially, once this global setting is enabled, it can be overridden by a specific credit limit set on an individual customer's contact record (under the Accounting tab). The individual limit always takes precedence over the global one.
- This enables a global credit limit check for all customers, triggering an alert if a new sales order or invoice would cause a customer to exceed their limit.
- Batch Payments:
- This feature allows you to group multiple customer payments into a single batch, generating a deposit slip with a unique reference.
- This is essential for efficient bank reconciliation, as it allows you to match a single batch deposit on your bank statement to numerous payments in Odoo. Crucially, for Australian businesses, make sure to enable this setting for companies that need to process vendor payments via ABA transfers, a vital function covered in Section 4.3
- This feature allows you to group multiple customer payments into a single batch, generating a deposit slip with a unique reference.
- Additional Customer Settings:
- Warnings: Enables alerts for specific customers. The warning message is configured on the customer's contact record under the internal notes tab.
- Customer Addresses: Allows you to define separate invoicing and delivery addresses for a customer, which is common in many business operations.
- Cash Rounding: Used in situations where cash payments must be rounded to the nearest five cents. Configuration involves setting a Rounding Precision, Rounding Strategy, and Rounding Method.
- Default Incoterm: Sets a default International Commercial Term (e.g., FOB, CIF) that is automatically populated on sales documents. This can be overridden on individual transactions.
- Warnings: Enables alerts for specific customers. The warning message is configured on the customer's contact record under the internal notes tab.
3.4 Identifying Irrelevant Customer Payment Settings
The settings for SEPA Direct Debit (SDD) and QR Codes found under the Customer Payments section are primarily designed for European businesses and are not relevant for Australian localization. These can be safely ignored.
Next, we will shift our focus from the customer side of the ledger to the corresponding settings for managing vendor bills and payments.
4.0 Vendor Bill and Payment Configuration
4.1 Strategic Importance of Vendor-Side Settings
Effective configuration of vendor bill and payment settings is key to a streamlined and cost-effective accounts payable process. These settings help reduce manual data entry, minimize errors, and ensure that suppliers are paid accurately and on time. This is not just an administrative function; it is vital for maintaining strong vendor relationships, avoiding late payment penalties, and capitalizing on early payment discount opportunities.
4.2 AI-Powered and Automated Bill Processing
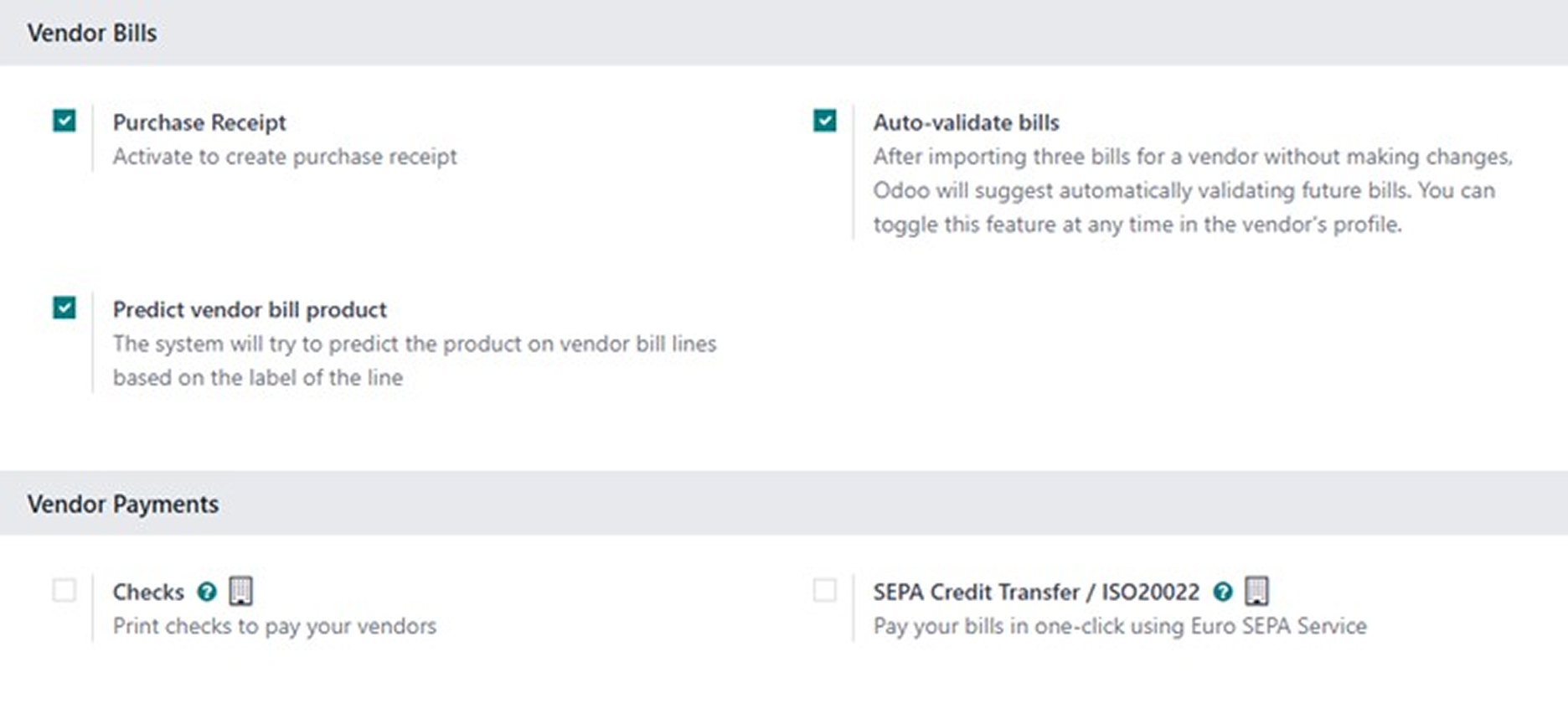
Odoo offers powerful features to automate the management of vendor bills.
- Predict Vendor Bill Product: This AI-powered feature learns from your past vendor bills. Based on the vendor and the text on the bill line, it can predict which product or expense account to use. This is particularly useful for recurring expenses, as it significantly speeds up data entry and reduces the risk of misclassification.
- Auto-validate Bills: This automation feature can suggest automatically validating future bills from a trusted vendor after you have imported and processed three of their bills without modification. This can also be enabled or disabled directly from the vendor's contact card (in the Accounting tab). It is ideal for recurring bills of the same amount or for long-term, trusted suppliers.
4.3 Vendor Payments and Australian Localization
While you will see settings like Checks and SEPA Credit Transfer, these are not relevant for Australian business practices. The Australian equivalent is automatically installed and configured.
- ABA Transfers: The ABA (Australian Bankers' Association) Transfer module is automatically installed as part of the Australian fiscal localization package. This module is the standard method for processing electronic payments to vendors in Australia. It allows you to create batch payments for multiple vendors at once and generate the required ABA file, which you can then upload to your online banking portal to execute the payments.
From managing vendor bills, we now move to the broader topic of converting all incoming documents into structured digital data.

5.0 Document Digitization (OCR)
5.1 Strategic Importance of Digitization
Document digitization leverages Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and AI to convert unstructured documents, like PDF vendor bills, into structured data within Odoo. The strategic value is immense: it dramatically reduces the hours spent on manual data entry, minimizes human error, and creates an efficient, paperless workflow for your accounts payable department, freeing up your team for more value-added analysis.
5.2 Configuring Digitization Options
The digitization service can be configured to suit your company's workflow.
- Vendor Bills & Customer Invoices: For both document types, you can select one of three operational modes:
- Do not digitize: The feature is disabled.
- Digitize on demand only: A "Digitize Document" button appears on uploaded documents, giving users manual control over when the OCR process is initiated.
- Digitize automatically: All uploaded documents are automatically sent for digitization as soon as they are added to the system.
- Single Invoice Line per Tax: If enabled, this option consolidates all items on the original document that share the same tax rate into a single line on the bill created in Odoo.
- Bank Statements: This feature can be used to read and create statement lines from an imported bank statement document (such as a PDF).
5.3 Service and Credit Information
It is important to understand the operational details of this service:
- IAP Service: Digitization is an In-App Purchase (IAP) service that requires prepaid credits to function.
- Credit Consumption: The digitization of one document consumes one credit.
- Free Credits: Odoo Enterprise users receive a number of free credits to test the service before purchasing more.
- XML Exception: XML files are processed for free and do not consume credits, as they already contain structured data that does not require OCR.
- Database-Specific Learning: A critical piece of expert knowledge to note is that the OCR and AI functionality improves over time as Odoo learns from the data entered. This learning is database-specific and does not take into account historical patterns from other databases, so managing expectations about its initial accuracy is key.
After configuring how external documents are processed, we will now look at the internal chart of accounts where the resulting financial data is posted.
6.0 Default Accounts and Stock Valuation
6.1 Strategic Importance of Default Accounts
Configuring default accounts is fundamental to creating a standardized and reliable accounting framework. These settings prevent countless manual journal corrections by ensuring that automated transactions—such as those from currency exchange differences or inventory movements—are posted correctly to the Chart of Accounts (COA). This maintains the integrity of your financial data and ensures that reports like the P&L and Balance Sheet are accurate and trustworthy without constant manual intervention.
6.2 Core Default Account Configuration
The default accounts are logically grouped to manage specific types of automated financial entries.
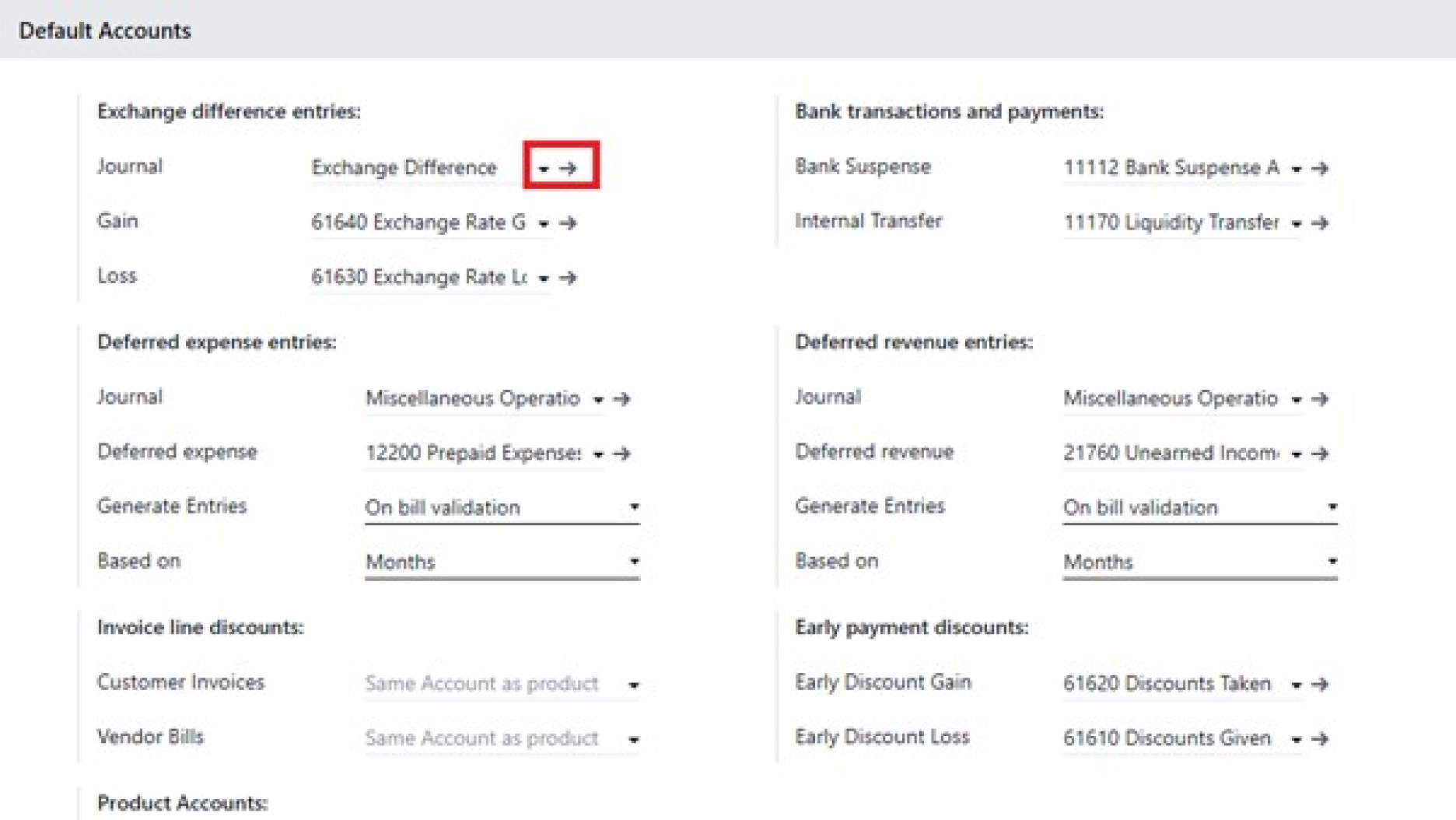
- Exchange Difference Entries:
- Gain account (Income type): Records gains resulting from favorable movements in exchange rates between the time a foreign currency bill is posted and when it is paid.
- Loss account (Expense type): Records losses resulting from unfavorable exchange rate movements.
- Gain account (Income type): Records gains resulting from favorable movements in exchange rates between the time a foreign currency bill is posted and when it is paid.
- Bank Transactions and Payments:
- Bank Suspense: This current asset account serves as a temporary holding account for transactions imported from a bank feed. Transactions sit here until they are reconciled against an invoice, bill, or another account.
- Internal Transfer: This acts as a clearing account for funds moved between your company's own bank accounts, ensuring the transfer is tracked correctly until it appears in both accounts.
- Bank Suspense: This current asset account serves as a temporary holding account for transactions imported from a bank feed. Transactions sit here until they are reconciled against an invoice, bill, or another account.
- Deferred Expense/Revenue Entries:
- These settings are used to manage prepaid expenses and deferred revenues, spreading their recognition over multiple accounting periods.
- The required accounts are a Prepaid Expense account (Current Asset type) and a Deferred Revenue account (Current Liability type).
- These settings are used to manage prepaid expenses and deferred revenues, spreading their recognition over multiple accounting periods.
- Discount Accounts:
- Invoice Line Discounts: The expense account used for posting discounts that are applied directly to individual lines on a customer invoice.
- Early Payment Discounts: These include a gain account (income type) for recording discounts received from vendors for paying early, and a loss account (expense type) used when the company incurs a loss due to delayed payments to vendors.
- Invoice Line Discounts: The expense account used for posting discounts that are applied directly to individual lines on a customer invoice.
6.3 General Account Properties and Hierarchy
Odoo uses a clear hierarchy to determine which income or expense account to use for a given transaction, providing both standardization and flexibility.
The default Income and Expense accounts set in this section serve as the ultimate fallback. However, more specific settings will override these defaults. The hierarchy, from lowest to highest priority, is:
- General Accounting Settings: The default income/expense accounts used if no other rule applies.
- Journal Level: A default income account set on the Customer Invoice journal or an expense account on the Vendor Bills journal will override the general setting.
- Product Category Level: Income/expense accounts defined on a product's category will override the journal-level accounts.
- Product Level: An income/expense account set directly on the product itself has the highest priority and will override all other settings.
6.4 Stock Valuation and Manufacturing Accounts
These settings are critical for businesses that manage physical inventory.
- Automatic Accounting: Enabling this feature ensures that financial accounts are updated in real-time as stock moves occur. This is essential for maintaining an accurate, perpetual inventory system. Key accounts to configure include:
- Stock Valuation Account (Current Asset type)
- Stock Input Account (A clearing account for the value of received stock)
- Stock Output Account (A clearing account for the value of delivered stock)
- Production Account (A temporary clearing account for manufacturing costs)
- WIP Account Properties: This section only appears if the manufacturing module is installed. It contains two temporary accounts to track costs during the production cycle:
- WIP Account (Work In Progress)
- WIP Overhead Account
With the internal accounting structure defined, we will finalize the setup by configuring bank data imports and fiscal periods.
7.0 Bank, Cash, and Fiscal Period Settings
7.1 Strategic Importance of Financial Period and Bank Settings
These settings form the structural foundation of your financial reporting. An incorrect fiscal year date can invalidate an entire year's worth of P&L reporting and lead to significant, costly rework during tax season. This is arguably one of the most critical settings in the entire system. Similarly, correctly configuring bank import formats is the first step toward an efficient bank reconciliation process, a cornerstone of financial control.
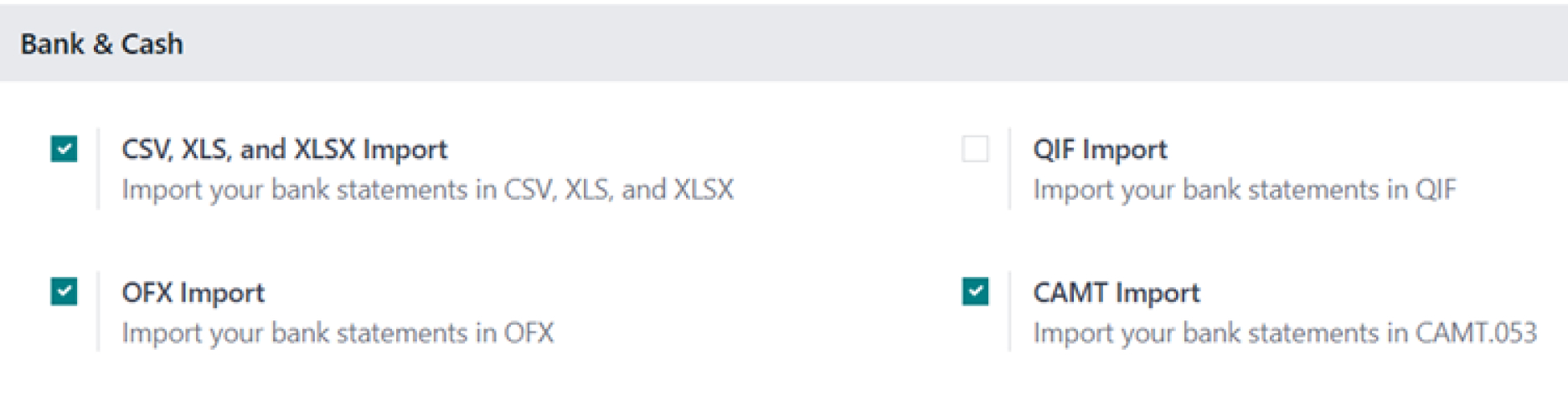
7.2 Bank & Cash Import Formats
Odoo supports several file formats for manually importing bank statements, allowing you to choose the one that best suits your bank's export capabilities. Supported formats include:
- CSV, XLS, and XLSX Import
- OFX Import
- QIF Import
- CAMT Import
7.3 Fiscal Period Configuration
These settings define your company's financial reporting periods and data visibility rules.
- Fiscal Year: This field must be set to the last day of your company's fiscal year. For most Australian businesses, this is June 30. This date is critical as it dictates the start and end dates for all financial reports. For example, with a June 30 year-end, the Balance Sheet for the 2025 financial year will reflect data up to June 30, 2026. While other fiscal year-ends are possible, they typically require approval from the ATO.
- Fiscal Years (Setting): This provides the flexibility to define fiscal years that are shorter or longer than the standard 12 months, which may be necessary in specific circumstances, such as a company's first year of operation.
- Invoicing Switch Threshold: A key best practice during a system migration is to leverage the Invoicing Switch Threshold. By setting a cut-off date, you can prevent a large number of old, irrelevant invoices from being posted to the general ledger, saving significant time and effort in cleaning up historical data.
- Dynamic Reports: Enabling this feature transforms your financial reports into interactive tools. It allows users to drill down from a summary figure on a report (like total revenue) to see the individual journal entries that make up that total, providing transparency and facilitating faster analysis.
Finally, we will explore the advanced settings that enable deeper financial analysis and planning.
8.0 Analytics, Reporting, and Budgeting
8.1 Strategic Importance of Analytics and Reporting
While core accounting ensures compliance and historical record-keeping, the tools in this section elevate your financial system into a strategic asset. Analytic accounting and budgeting move you beyond basic bookkeeping to provide deep insights into profitability, performance, and financial planning. This enables proactive, data-driven decision-making rather than reactive financial management.
8.2 Configuring Analytic Accounting
Enabling Analytic Accounting allows you to track costs and revenues beyond the standard Chart of Accounts. It is used to analyze the profitability of specific projects, departments, cost centers, or product lines. When enabled, the following configuration items become available under the Accounting menu:
- Analytic Plans: Used to group related analytic accounts (e.g., a plan for "Client Projects").
- Analytic Accounts: The specific accounts used for detailed cost and revenue tracking (e.g., "Project A," "Project B").
- Analytic Distribution Models: Rules to automatically distribute a single expense or revenue line across multiple analytic accounts based on predefined percentages.
8.3 Implementing Budget Management
Odoo allows you to manage two distinct types of budgets, both of which are enabled by this setting.
- Analytic Budgets: These budgets are used to track financial performance against specific analytic accounts, making them ideal for managing the budgets of internal projects or departments.
- To create: Navigate to Accounting ‣ Accounting ‣ Analytic Budgets and click New. Fill in the budget name and period. Under the Budget Lines tab, click Add a line to structure the budget using your previously created analytic plans and accounts. Enter the planned amounts in the Budgeted column and click Open to activate it.
- To create: Navigate to Accounting ‣ Accounting ‣ Analytic Budgets and click New. Fill in the budget name and period. Under the Budget Lines tab, click Add a line to structure the budget using your previously created analytic plans and accounts. Enter the planned amounts in the Budgeted column and click Open to activate it.
- Financial Budgets: These budgets are used for official financial reporting and are based on the main Chart of Accounts (i.e., your income and expense accounts).
- To create: Navigate to Accounting ‣ Reporting ‣ Profit and Loss. First, select the desired reporting period. Then, click the Budget button and enter a name for your budget. A new column will appear next to the Balance column, allowing you to enter planned amounts directly against each relevant account. Odoo will automatically display a % column to show the comparison between budget and actual results.
8.4 Enhancing Document Readability
The Add totals below sections setting is a simple but effective feature for improving the clarity of complex documents. It allows you to add section breaks within Sales Orders or Invoices to group line items. When the document is printed, each section will display its own subtotal, making it much easier for customers to read and understand.
9.0 Conclusion
While Odoo's Australian fiscal localization package provides a powerful and compliant starting point, the true value of the system is unlocked through the thoughtful configuration of its detailed settings.
By carefully reviewing and tailoring the options covered in this guide—from tax and currency management to customer payments and analytic budgeting—you ensure the system is perfectly aligned with your company's unique operational needs.
This process transforms Odoo from a generic accounting tool into a customized platform that drives efficiency, ensures compliance, and delivers valuable business insights.
The information and tips shared on this blog are meant to be used as learning and personal development tools as you launch, run and grow your business. While a good place to start, these articles should not take the place of personalised advice from professionals. As our lawyers would say: “All content on WAO’s blog is intended for informational purposes only. It should not be considered legal or financial advice.” Additionally, WAO is the legal copyright holder of all materials on the blog, and others cannot re-use or publish it without our written consent.


